Summary:
Tracking your menstrual cycle is an important tool for optimizing your fertility. By understanding your body’s natural rhythms and changes, you can increase your chances of getting pregnant. In this step-by-step guide, we will go through the key components of tracking your menstrual cycle and how to use this information to optimize your fertility.
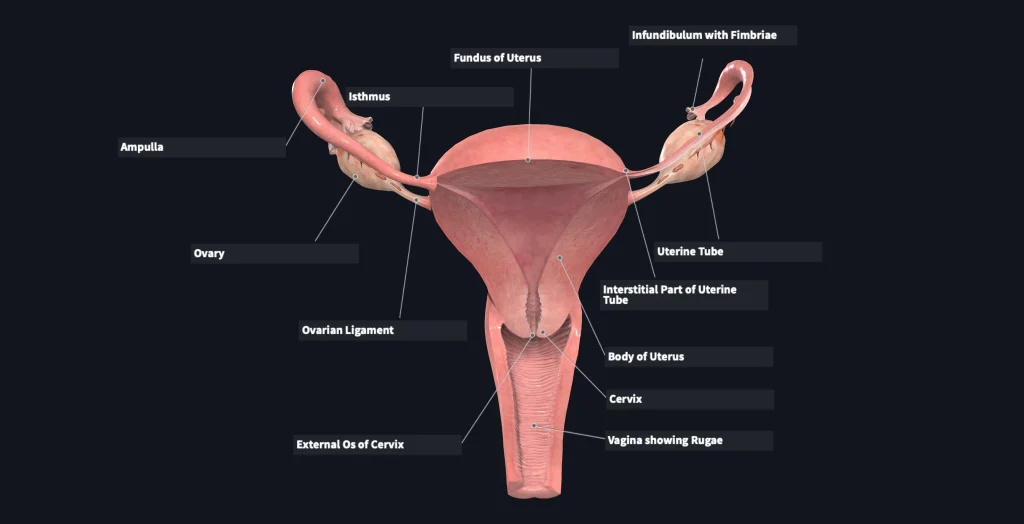
First, it’s important to understand the basics of your menstrual cycle. The menstrual cycle is the monthly process your body goes through to prepare for pregnancy. It is controlled by hormones and consists of three phases: the follicular phase, ovulation, and the luteal phase. The average menstrual cycle is 28 days, but can range from 21 to 35 days.
The first step in tracking your menstrual cycle is to start a menstrual calendar. This can be done on paper or using a menstrual tracking app. Record the first day of your period as day one, and continue tracking until the first day of your next period. This will give you an overview of the length of your cycle and help you identify patterns.
The next step is to track your basal body temperature (BBT). This is your body’s temperature at rest and can be measured with a special basal thermometer. Your BBT will rise slightly after ovulation, indicating that you have ovulated. By tracking your BBT over a few months, you can determine when you are most likely to ovulate. This is important because you are most fertile in the days leading up to and including ovulation.
Another important aspect of tracking your menstrual cycle is monitoring changes in your cervical mucus. Leading up to ovulation, your cervical mucus will become clear, thin, and stretchy. This is known as “egg white” cervical mucus and is the most fertile type. By tracking these changes, you can identify your most fertile days.
A Step-by-Step Guide to Tracking Your Menstrual Cycle for Optimal Fertility
In addition to tracking your BBT and cervical mucus, you can also use ovulation predictor kits (OPKs) to pinpoint your most fertile days. These tests detect the surge of luteinizing hormone (LH) that occurs right before ovulation. By tracking your BBT, cervical mucus, and using OPKs, you can get a comprehensive understanding of your menstrual cycle and increase your chances of conception.
It’s also important to pay attention to any other physical or emotional changes you experience during your cycle. For example, some women may experience breast tenderness or bloating around ovulation, while others may have mood changes. These can also be helpful indicators of ovulation and fertility.
Once you have been tracking your menstrual cycle for several months, you can use this information to predict when you are most likely to ovulate. This is important for timing intercourse and increasing your chances of pregnancy. Generally, the five days leading up to ovulation and the day of ovulation itself are considered the most fertile days.
It’s important to note that tracking your menstrual cycle is not a foolproof method of birth control. While it can help you determine when you are most likely to get pregnant, it should not be relied upon as the only method of contraception.
In summary, tracking your menstrual cycle is a crucial component of optimizing your fertility. By understanding the different phases of your cycle and tracking changes in your body, you can determine when you are most fertile and increase your chances of getting pregnant. Be sure to track your menstrual cycle for several months to establish patterns and use this information to pinpoint your most fertile days. If you are struggling to conceive, tracking your menstrual cycle can also provide valuable information for your doctor to help determine any underlying fertility issues.
5 Probable Search Queries:
1. “How to track my menstrual cycle for fertility”
2. “Basal body temperature tracking for fertility”
3. “Using ovulation predictor kits to optimize fertility”
4. “The importance of cervical mucus in tracking fertility”
5. “How tracking my menstrual cycle can increase my chances of getting pregnant”