The Art of Charting: Using Your Cycle to Increase Fertility
When it comes to trying to conceive, many couples are looking for ways to increase their chances of success. While there are various medical interventions available, some couples prefer to try natural methods first. One method that has been gaining popularity is charting, also known as fertility tracking or fertility awareness. This practice involves tracking various signs and symptoms of a woman’s menstrual cycle to determine the most fertile days for conception. In this blog post, we will delve into the art of charting and how it can be used to increase fertility.
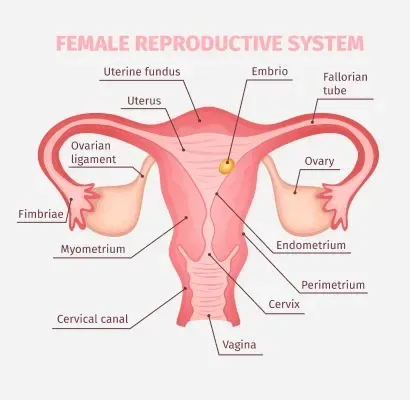
First, let’s understand the basics of a woman’s menstrual cycle. On average, a menstrual cycle lasts for 28 days, with the first day of bleeding being considered day one. During this time, the body goes through various hormonal changes that prepare it for pregnancy. The first half of the cycle is known as the follicular phase, where the follicles in the ovaries develop and produce estrogen. This hormone helps thicken the uterine lining, getting it ready for a potential pregnancy. Around day 14, the ovary releases an egg in a process called ovulation. This is the most fertile time of the cycle, as the egg can be fertilized by sperm. If fertilization does not occur, the body enters the luteal phase, where the uterine lining starts to shed, resulting in menstruation.
Now that we have a basic understanding of the menstrual cycle, let’s explore how charting can help increase fertility. Charting involves tracking various signs and symptoms of the menstrual cycle, such as basal body temperature, cervical mucus, and cervical position. These signs can provide valuable information about a woman’s fertility and help determine the most fertile days for conception.
Basal body temperature (BBT) is a woman’s temperature when at rest. During the first half of the cycle, BBT is relatively low, but after ovulation, it rises due to the release of progesterone. Tracking BBT can help pinpoint the day of ovulation, as the temperature spike is a clear indication that ovulation has occurred. This information is crucial for couples trying to conceive, as they can time intercourse around the most fertile days.
Cervical mucus is another essential factor in charting. This fluid is produced by the cervix and changes throughout the menstrual cycle. During the fertile days, the mucus becomes thin, stretchy, and clear, resembling the consistency of egg whites. This type of mucus helps sperm travel through the cervix and into the uterus, increasing the chances of fertilization. By tracking changes in cervical mucus, couples can identify their most fertile days and plan accordingly.
Cervical position is also a crucial factor in charting. The cervix changes position and texture throughout the menstrual cycle, with the most significant changes occurring during ovulation. During the fertile days, the cervix becomes softer, higher, and more open to allow sperm to enter. By tracking these changes, couples can again pinpoint their most fertile days.
The Art of Charting: Using Your Cycle to Increase Fertility
In addition to tracking these signs, there are various methods of charting that couples can use. The most popular method is the symptothermal method, which involves tracking BBT, cervical mucus, and cervical position. Other methods include the calendar method, where a woman tracks her cycle length over several months to predict ovulation, and the ovulation predictor kit method, which uses urine tests to detect the surge in luteinizing hormone (LH) that occurs before ovulation.
Now that we understand the basics of charting and how it can help increase fertility let’s address some common questions and concerns.
1. Can charting be used as a form of birth control?
While charting can be an effective method of natural birth control, it is not recommended as a sole form of contraception. It requires a lot of diligence and consistency, and even then, there is always a risk of pregnancy. It’s essential to use other forms of birth control if avoiding pregnancy is the goal.
2. Is charting only for women with regular cycles?
No, charting can be beneficial for women with irregular cycles as well. By tracking signs and symptoms, women with irregular cycles can identify patterns and better predict when ovulation may occur.
3. Can stress affect the accuracy of charting?
Stress can affect a woman’s menstrual cycle, which can, in turn, affect the accuracy of charting. However, by consistently tracking and being aware of the signs, stress can be managed, and the accuracy of charting can be improved.
4. Can charting help identify underlying fertility issues?
Yes, charting can provide valuable information that can help identify underlying fertility issues. By tracking BBT and other signs, women can identify if ovulation is occurring regularly and if there are any issues with the length of the luteal phase. This information can be helpful when discussing fertility concerns with a doctor.
5. What other factors can affect fertility?
Aside from the menstrual cycle, other factors can affect fertility, such as age, weight, diet, and overall health. It’s essential to take care of your body and address any underlying health issues to increase fertility.
In summary, the art of charting can be a helpful tool for couples trying to conceive. By tracking various signs and symptoms of the menstrual cycle, women can identify their most fertile days and increase their chances of pregnancy. However, it’s crucial to remember that charting is not a foolproof method, and it’s always best to consult with a doctor for any fertility concerns. By combining charting with a healthy lifestyle, couples can increase their chances of conceiving and start their journey towards parenthood.