From Ovulation to Pregnancy: A Step-by-Step Guide to Monitoring
Are you and your partner trying to start a family? Are you looking for ways to increase your chances of getting pregnant? If so, understanding your ovulation cycle and monitoring it closely can greatly improve your chances of conceiving. In this post, we will discuss the step-by-step process of monitoring ovulation and how it can lead to a successful pregnancy.
Understanding Ovulation
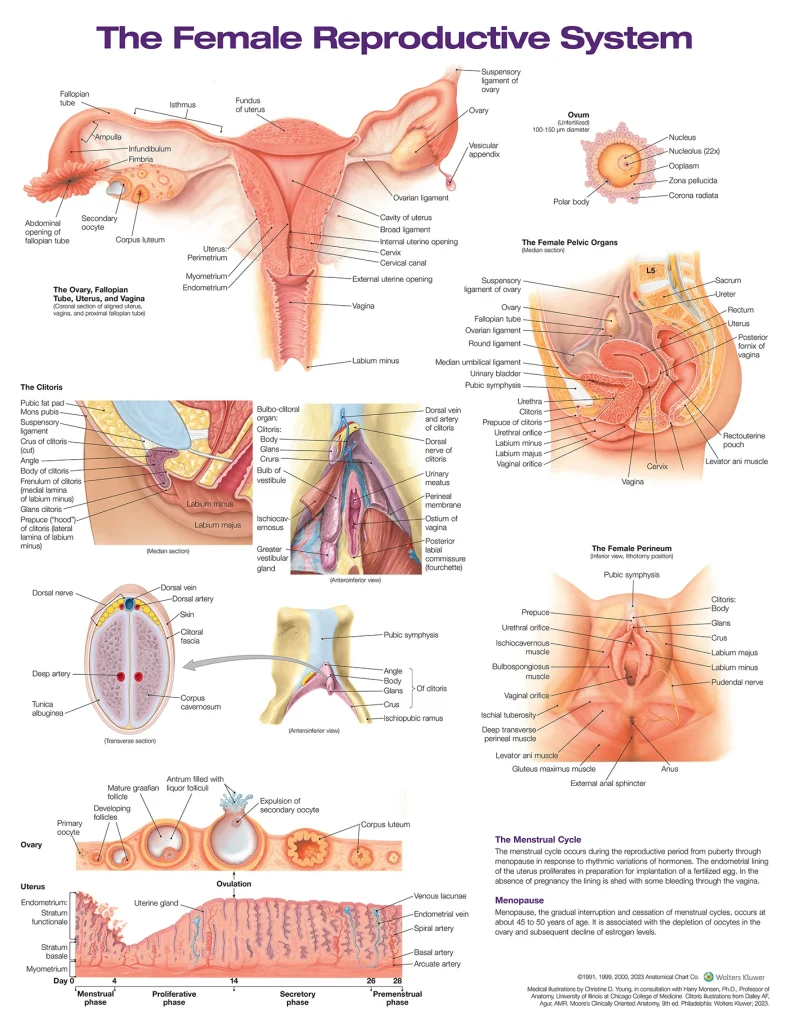
Before we dive into monitoring ovulation, it’s important to understand what it is and how it affects your chances of getting pregnant. Ovulation is the process in which a mature egg is released from the ovary and travels down the fallopian tube, where it may be fertilized by sperm. This usually happens once a month, around day 14 of a 28-day menstrual cycle.
Tracking Your Menstrual Cycle
The first step in monitoring ovulation is to track your menstrual cycle. This will help you determine when you are most likely to ovulate. The average menstrual cycle is 28 days, but it can vary from person to person. It’s important to keep track of your cycle for a few months to get a better understanding of its length and regularity.
There are many ways to track your menstrual cycle, including using a calendar or a period-tracking app. Some apps even allow you to track other symptoms such as changes in cervical mucus and basal body temperature, which can also indicate ovulation.
Monitoring Changes in Cervical Mucus
Cervical mucus, also known as cervical fluid, plays a crucial role in the ovulation process. As your body prepares for ovulation, your cervical mucus changes in consistency and texture. It becomes clearer, thinner, and more slippery, resembling the consistency of egg whites. This type of mucus helps sperm travel through the cervix and up to the fallopian tubes to fertilize the egg.
By monitoring changes in your cervical mucus, you can determine when you are most fertile. This usually happens a few days before ovulation and can last up to a day after ovulation. You can check your cervical mucus by placing a clean finger inside your vagina and checking the consistency and texture of the mucus.
Using Ovulation Predictor Kits
Ovulation predictor kits (OPKs) are another useful tool in monitoring ovulation. These kits work by detecting the surge of luteinizing hormone (LH) in your urine, which happens a day or two before ovulation. The surge in LH triggers the release of the egg from the ovary.
From Ovulation to Pregnancy: A Step-by-Step Guide to Monitoring
OPKs are easy to use and can be purchased at most drugstores. They come with test strips or digital tests that you can use to detect the LH surge. It’s recommended to start testing a few days before you expect to ovulate, as the surge can happen quickly and may be missed if you start testing too late.
Tracking Basal Body Temperature
Basal body temperature (BBT) refers to your body’s temperature at rest. During ovulation, your BBT rises slightly due to an increase in progesterone, a hormone that is released after ovulation. By tracking your BBT, you can determine when you have ovulated and when your most fertile days are.
To track your BBT, you will need a basal body thermometer. This is a special thermometer that is more sensitive and can detect small changes in your body temperature. You will need to take your temperature first thing in the morning before getting out of bed and record it on a chart or in a tracking app. A rise in temperature of about 0.5 to 1 degree Fahrenheit can indicate ovulation.
Monitoring Other Signs and Symptoms
In addition to tracking your menstrual cycle and using various monitoring methods, there are other signs and symptoms you can pay attention to that may indicate ovulation. These include:
– Light spotting or cramping: Some women may experience light spotting or cramping around the time of ovulation.
– Changes in libido: You may notice an increase in your sex drive around the time of ovulation.
– Breast tenderness: Some women may experience breast tenderness or swelling around ovulation.
– Mittelschmerz: This is a German term that means “middle pain.” It refers to a sharp or cramp-like pain on one side of the lower abdomen, which may occur around the time of ovulation.
Combining all these methods of monitoring can give you a more accurate picture of when you are ovulating and when you are most likely to conceive.
Summary:
Monitoring ovulation is a crucial step in increasing your chances of getting pregnant. By tracking your menstrual cycle, monitoring changes in cervical mucus, using ovulation predictor kits, tracking basal body temperature, and paying attention to other signs and symptoms, you can determine when you are most fertile and plan accordingly. It’s important to keep in mind that every woman’s body is different, and it may take a few months of monitoring to understand your cycle fully. But with patience and consistency, you can improve your chances of conceiving and start your journey towards parenthood.
Search Queries:
1. “How to monitor ovulation for pregnancy”
2. “Best methods for tracking ovulation”
3. “Ovulation predictor kits: How do they work?”
4. “Basal body temperature tracking for ovulation”
5. “Signs and symptoms of ovulation to watch for”