Ovulation is a crucial part of a woman’s reproductive cycle that occurs once per month. It is the process where an egg is released from the ovary and travels down the fallopian tube, waiting to be fertilized by sperm. This is the key event in a woman’s fertility, as it is the only time when she can become pregnant. Therefore, understanding ovulation and monitoring it is essential for those who are trying to conceive or simply want to track their menstrual cycle.
In this beginner’s guide, we will cover everything you need to know about ovulation monitoring, including what ovulation is, how to track it, and the various methods available. We will also discuss the signs and symptoms of ovulation, the importance of tracking your menstrual cycle, and how to use this information to increase your chances of conception.
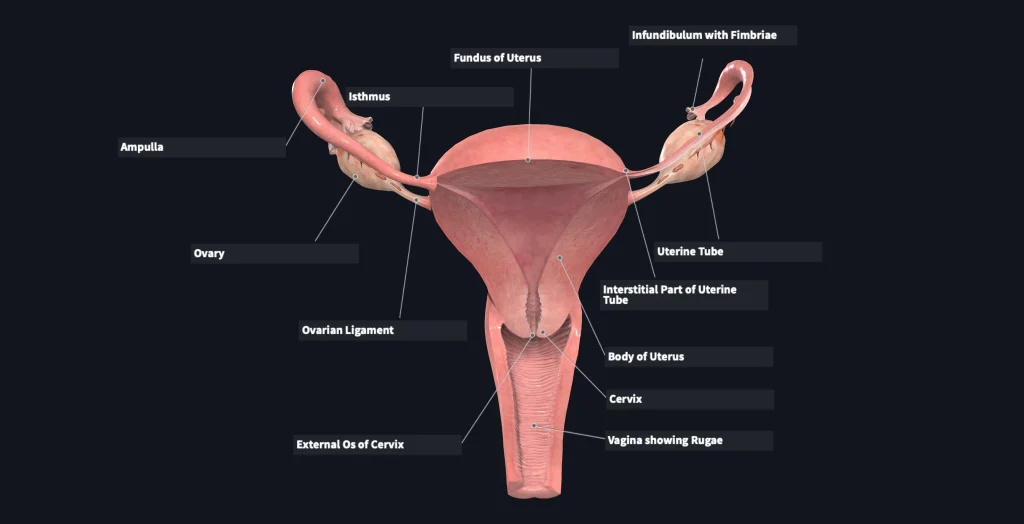
What is Ovulation?
Ovulation is the process where a mature egg is released from the ovary and travels down the fallopian tube. This usually occurs around day 14 of a 28-day menstrual cycle. However, every woman’s cycle is different, and ovulation can occur at different times for each individual. Once the egg is released, it has a lifespan of 12-24 hours, waiting to be fertilized by sperm. If the egg is not fertilized, it will disintegrate, and the uterus will shed its lining, resulting in menstruation.
Why is Ovulation Monitoring Important?
Ovulation monitoring is crucial for those trying to conceive, as it helps them determine the best time to have intercourse to increase their chances of getting pregnant. It is also essential for those who want to track their menstrual cycle for health reasons. By monitoring ovulation, women can understand their body’s natural rhythm and detect any irregularities in their cycle, which could indicate potential health issues.
Signs and Symptoms of Ovulation
There are various signs and symptoms that can indicate ovulation. These include:
1. Changes in cervical mucus: As ovulation approaches, the body produces more estrogen, causing changes in the cervical mucus. It becomes thin, clear, and slippery, similar to raw egg whites, making it easier for sperm to travel to the egg.
2. Basal body temperature (BBT) rise: BBT is the lowest body temperature recorded during rest. After ovulation, a woman’s BBT will increase by 0.5 to 1 degree Fahrenheit, indicating that ovulation has occurred.
3. Ovulation pain: Some women experience mild cramping on one side of their abdomen during ovulation. This pain is known as Mittelschmerz, which is a German word meaning “middle pain.”
4. Breast tenderness: Due to hormonal changes, some women may experience breast tenderness during ovulation. This symptom is similar to what women feel before their period.
5. Increased sex drive: As the body prepares for ovulation, it produces more estrogen, which can increase a woman’s sex drive.
Ovulation Monitoring 101: A Beginner's Guide
Methods of Ovulation Monitoring
There are several methods available for monitoring ovulation. These include:
1. Ovulation predictor kits (OPKs): These kits detect the surge of luteinizing hormone (LH) in a woman’s urine, which occurs 12-36 hours before ovulation. Once the kit shows a positive result, ovulation is likely to occur within the next 24-48 hours.
2. Basal body temperature (BBT) charting: As mentioned earlier, a woman’s BBT rises after ovulation. By tracking this temperature every morning before getting out of bed, women can determine when they have ovulated.
3. Cervical mucus monitoring: As ovulation approaches, cervical mucus becomes thin, clear, and slippery. By tracking changes in the mucus throughout the cycle, women can determine when they are most fertile.
4. Ovulation tracking apps: There are various smartphone apps available that can help women track their ovulation. These apps use data such as menstrual cycle length, BBT, and cervical mucus to predict when ovulation will occur.
5. Ovulation monitoring devices: There are also devices available, such as fertility monitors, that use advanced technology to track ovulation. These devices may monitor multiple signs of ovulation, including BBT, LH levels, and electrolyte levels in saliva.
Using Ovulation Monitoring for Conception
For those trying to conceive, ovulation monitoring can significantly increase their chances of getting pregnant. By determining when ovulation is likely to occur, couples can time intercourse around this time, increasing the chances of sperm fertilizing the egg. It is also essential to have intercourse a few days before ovulation, as sperm can survive in the reproductive tract for up to five days.
In addition to timing intercourse, ovulation monitoring can also help identify any potential issues with ovulation. If a woman is not ovulating, she will not be able to get pregnant. By tracking ovulation and consulting with a healthcare professional if there are any concerns, women can take appropriate measures to improve their fertility.
Conclusion
Ovulation is a crucial part of a woman’s reproductive cycle, and monitoring it is essential for those trying to conceive or tracking their menstrual cycle. By understanding what ovulation is, the signs and symptoms, and the various methods available for monitoring it, women can take control of their reproductive health and increase their chances of getting pregnant.
SEO metadata: