In recent years, there has been a rise in the number of women facing fertility challenges, specifically low ovarian reserve. This can be a daunting experience for women who are hoping to conceive, but there are options available for those who want to try to achieve pregnancy on their own. One of these options is self-insemination, a process in which a woman can use donor sperm to inseminate herself at home. This can be a more affordable and less invasive option for women with low ovarian reserve who may not be able to undergo traditional fertility treatments. In this step-by-step guide, we will explore the process of self-insemination and provide helpful tips for women with low ovarian reserve who are considering this method.
Before we dive into the steps of self-insemination, it is important to understand what low ovarian reserve means and how it can affect fertility. Low ovarian reserve is a condition in which a woman’s ovaries have a reduced number of eggs and may not respond well to fertility medications. This can make it difficult for women to conceive, as the quality and quantity of their eggs may be compromised. Low ovarian reserve is often associated with advanced maternal age, but it can also occur in younger women due to factors such as genetic predisposition, medical treatments, or lifestyle choices.
Now, let’s take a look at the step-by-step guide to self-insemination for women with low ovarian reserve:
Step 1: Understand the Legalities and Risks
Before beginning the process of self-insemination, it is important to understand the legalities and risks involved. Depending on where you live, there may be laws and regulations surrounding self-insemination and the use of donor sperm. It is recommended to consult with a lawyer or seek legal advice to ensure that you are following all necessary protocols and protecting yourself and your future child. Additionally, there are potential risks associated with self-insemination, such as infection or allergic reactions to the donor sperm. It is important to research and understand these risks before proceeding.
Step 2: Choose a Donor
The next step in self-insemination is to choose a donor. Some women may have a known donor, such as a friend or family member, while others may choose to purchase donor sperm from a reputable sperm bank. When selecting a sperm donor, it is important to consider factors such as physical characteristics, medical history, and personal preferences. It is also recommended to undergo genetic testing to ensure that there are no potential health risks for you or your future child.
Step 3: Track Your Ovulation
Timing is crucial for self-insemination to be successful. It is important to track your ovulation cycle and determine when you are most fertile. This can be done through methods such as tracking your basal body temperature, using ovulation predictor kits, or monitoring changes in cervical mucus. Keeping track of your ovulation can help increase the chances of successful insemination.
A Step-by-Step Guide to Self-Insemination for Women with Low Ovarian Reserve
Step 4: Prepare the Materials
Before beginning the insemination process, it is important to have all necessary materials on hand. These may include a sterile syringe, a cup to hold the semen, and a speculum to help with insertion. It is recommended to purchase these materials from a reputable medical supplier to ensure safety and effectiveness.
Step 5: Insemination Process
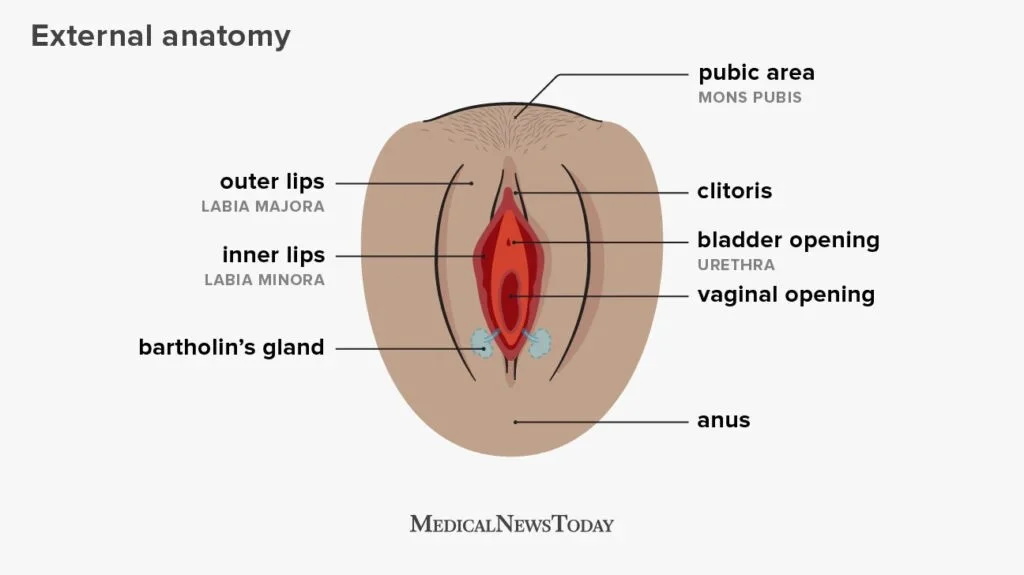
Now for the insemination process itself. Begin by washing your hands and sterilizing all materials. Collect the semen sample in the cup and use the syringe to draw up the desired amount. Carefully insert the syringe into the vagina and deposit the semen near the cervix. Some women may choose to use a speculum to help with insertion. After insemination, it is recommended to lie down for 15-20 minutes to allow the sperm to reach the cervix.
Step 6: Wait for Results
After insemination, it is important to wait and see if pregnancy occurs. It may take a few weeks to know for sure, so it is best to remain patient and not become discouraged if it does not happen right away. If pregnancy does not occur after a few attempts, it may be beneficial to consult with a fertility specialist for further guidance.
Self-insemination can be a helpful and empowering option for women with low ovarian reserve. However, it is important to remember that it may not be successful for everyone and there are other options available. It is always recommended to consult with a healthcare professional before making any decisions regarding fertility.
In conclusion, self-insemination is a potential option for women with low ovarian reserve who are looking to conceive. By understanding the legalities and risks, choosing a donor, tracking ovulation, and properly preparing for the insemination process, women can increase their chances of success. Remember to always seek advice from a healthcare professional and stay positive throughout the journey.
SEO metadata: