The Role of Age in Self-Insemination: A Comprehensive Analysis
Self-insemination, also known as self-fertilization or self-impregnation, is a method of conception where a person uses their own sperm or egg to impregnate themselves. This process has gained popularity in recent years as more people are choosing to become single parents or are struggling with fertility issues. However, one factor that is often overlooked in discussions about self-insemination is age. In this blog post, we will take a closer look at the role of age in self-insemination and its potential impact on the success and safety of this process.
To begin with, it is important to understand the biological factors at play when it comes to self-insemination and age. Women are born with a finite number of eggs, and as they age, the quality and quantity of these eggs decrease. This means that older women may have a harder time conceiving using their own eggs, whether through traditional methods or self-insemination. On the other hand, men produce new sperm throughout their lifetime, but the quality of sperm can also decline with age, potentially affecting the success of self-insemination.
One of the main reasons why age is a crucial factor in self-insemination is the increased risk of genetic abnormalities in offspring. As women age, the risk of chromosomal abnormalities, such as Down syndrome, increases. This risk also applies to self-insemination, as the eggs used for self-insemination are the same ones that would be used in traditional conception. Similarly, men over the age of 40 have a higher chance of fathering children with genetic disorders. This is something to consider for those who are planning on using their own sperm for self-insemination.
In addition to genetic risks, there are also potential health risks associated with self-insemination at an older age. For women, pregnancy and childbirth can be physically demanding, and the risks increase with age. Older women may be more likely to experience complications such as high blood pressure, gestational diabetes, or even preterm labor. Similarly, men may also face health risks if they choose to use their own sperm for self-insemination at an older age. Some studies have shown a higher risk of certain cancers in men who father children later in life.
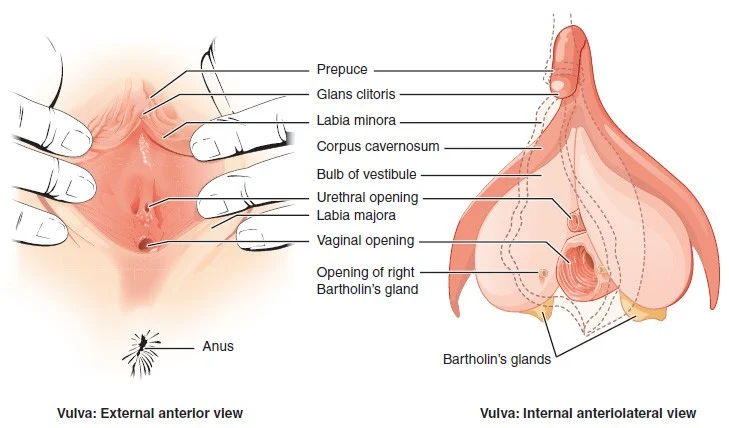
The Role of Age in Self-Insemination: A Comprehensive Analysis
Aside from the biological and health risks, age can also play a role in the success of self-insemination. As mentioned earlier, the quality and quantity of eggs and sperm decline with age, which can make it more difficult to conceive. This is especially true for women, as their fertility peaks in their 20s and starts to decline in their 30s. For those using their own sperm, studies have also shown that sperm quality decreases with age, potentially affecting the chances of successful self-insemination.
However, it is important to note that age is not the only factor that affects the success of self-insemination. Other factors such as overall health, lifestyle, and underlying fertility issues can also play a significant role. It is crucial for individuals considering self-insemination to consult with a healthcare professional and undergo thorough testing to determine their chances of success.
Another aspect that needs to be considered when discussing the role of age in self-insemination is the emotional and psychological impact. For many, self-insemination is a deeply personal and emotional decision, and age can add an extra layer of complexity to this process. Women may feel pressure to conceive at a younger age due to societal expectations, while older men may face judgment for becoming fathers later in life. It is essential for individuals to carefully consider their emotional readiness for self-insemination, regardless of their age.
In conclusion, age is a crucial factor when it comes to self-insemination. It can affect the biological, health, and emotional aspects of this process, and it is essential for individuals to understand and consider these factors before making a decision. While self-insemination can be a viable option for some, it is not a one-size-fits-all solution, and age should be carefully evaluated in conjunction with other relevant factors.
Search Queries:
1. “What is the impact of age in self-insemination?”
2. “Can older women successfully self-inseminate?”
3. “Are there health risks associated with self-insemination at an older age?”
4. “How does age affect the success of self-insemination?”
5. “What are the emotional considerations for self-insemination at different ages?”
Summary: Age is a crucial factor in self-insemination, as it can affect the biological, health, and emotional aspects of this process. Women’s egg quality and quantity decrease with age, increasing the risk of genetic abnormalities and complications during pregnancy. Men’s sperm quality can also decline with age, potentially affecting the success of self-insemination. Age should be carefully evaluated in conjunction with other relevant factors before making a decision about self-insemination.