Timing for Two: The Role of Synchronization in Self-Insemination
Self-insemination, also known as self-fertilization, is the process of a female organism fertilizing her own eggs without the presence of a male partner. This method is commonly observed in plants and some animal species, but it is also possible in humans. While self-insemination is not a common reproductive strategy in humans, it has gained attention in recent years as an alternative for same-sex couples and single women who want to conceive. One crucial factor that plays a significant role in self-insemination is synchronization, or the timing of the insemination process. In this blog post, we will explore the importance of synchronization in self-insemination and how it can impact the success of this method.
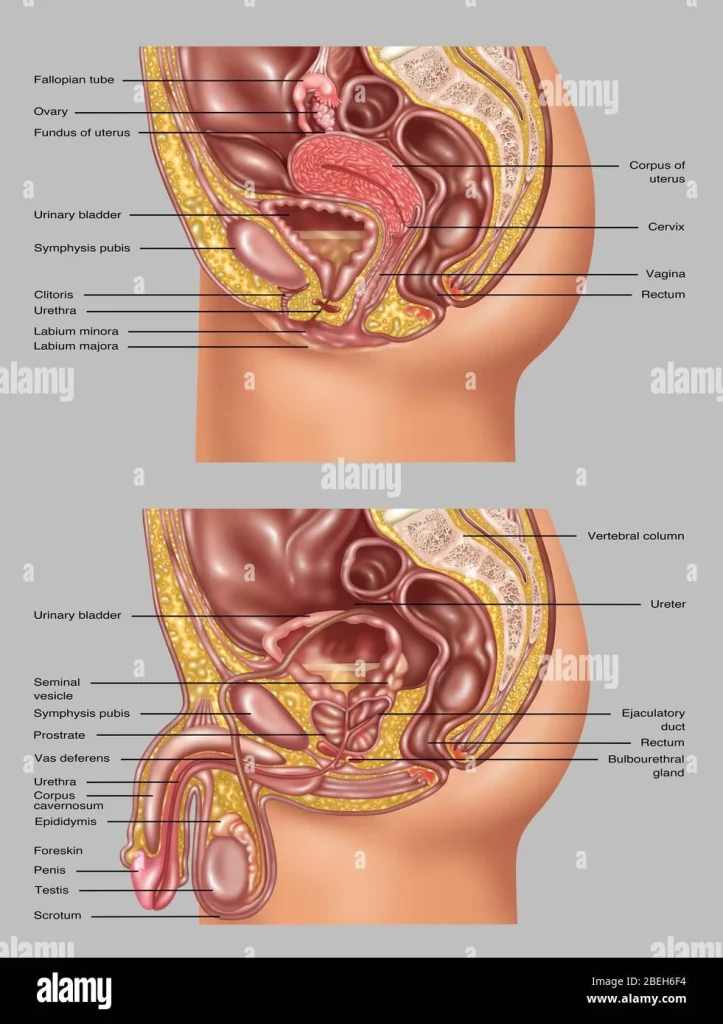
To understand the role of synchronization in self-insemination, we must first delve into the process of self-insemination itself. In humans, self-insemination can occur through the use of a syringe or a specialized device called an insemination kit. The process involves collecting semen from a donor or partner and inserting it into the vagina near the cervix. The goal is for the sperm to reach the fallopian tubes and fertilize the egg. However, for this to happen, synchronization between the sperm and the egg is crucial.
Synchronization in self-insemination refers to the alignment of the female’s ovulation cycle with the presence of viable sperm in the reproductive tract. Sperm can survive in the female reproductive tract for up to five days, while an egg is only viable for about 24 hours. Therefore, timing is crucial in self-insemination, as the sperm must be present in the reproductive tract during ovulation for fertilization to occur.
The timing of self-insemination can be challenging to predict, as it can vary from woman to woman and cycle to cycle. In natural conception, synchronization occurs naturally, as the male ejaculates during intercourse, and the sperm reaches the egg in the fallopian tubes. However, in self-insemination, the timing must be carefully planned and coordinated to increase the chances of success.
Timing for Two: The Role of Synchronization in Self-Insemination
One way to increase synchronization in self-insemination is through the use of ovulation prediction kits (OPKs). These kits detect the surge in luteinizing hormone (LH) in the body, which signals the release of an egg for ovulation. By tracking the LH surge, women can pinpoint the best time for self-insemination and increase the chances of fertilization.
Another method to improve synchronization in self-insemination is through the use of fertility tracking apps. These apps allow women to track their menstrual cycles, including ovulation, and can provide predictions for future cycles. By inputting information such as basal body temperature and cervical mucus changes, these apps can help women determine the best time for self-insemination.
Besides using OPKs and fertility tracking apps, there are other ways to increase synchronization in self-insemination. One method is through the use of fertility supplements, such as folic acid, zinc, and vitamin D. These supplements can help regulate hormonal levels and improve the quality of sperm and eggs, increasing the chances of successful fertilization. Additionally, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular exercise, can also contribute to synchronization and improve overall fertility.
While synchronization is essential in self-insemination, it is not the only factor that can impact its success. Other factors such as sperm and egg quality, cervical mucus, and the environment of the reproductive tract can also affect the outcome. It is crucial to consider these factors and address any potential issues before attempting self-insemination.
In conclusion, synchronization plays a crucial role in self-insemination, as it determines the alignment of the female’s ovulation cycle with the presence of viable sperm. By carefully planning and tracking ovulation, women can increase their chances of successful fertilization through self-insemination. However, it is essential to note that synchronization is not the only factor to consider, and it is crucial to address any potential issues that may affect the success of self-insemination.
Search Queries:
1. How does synchronization impact self-insemination?
2. What is the role of timing in self-insemination?
3. What methods can be used to improve synchronization in self-insemination?
4. Can fertility tracking apps help with synchronization in self-insemination?
5. What factors besides synchronization can affect the success of self-insemination?