Break the Biological Barrier: The Science Behind Self-Insemination for Single Women
In the past, starting a family was predominantly seen as a task for couples. However, with the rise of women empowerment and the evolution of reproductive technology, single women now have the option to become mothers on their own. One of the methods available for single women is self-insemination, which allows them to conceive without the need for a partner or medical intervention.
Self-insemination is a process that involves collecting and inserting sperm into the vagina or uterus in order to fertilize an egg. This can be done through various methods such as using a syringe, cervical cap, or a specially designed insemination kit. While it may seem like a simple process, there is actually a lot of science behind it. In this blog post, we will delve into the details of self-insemination for single women and how it works.
Understanding the Female Reproductive System
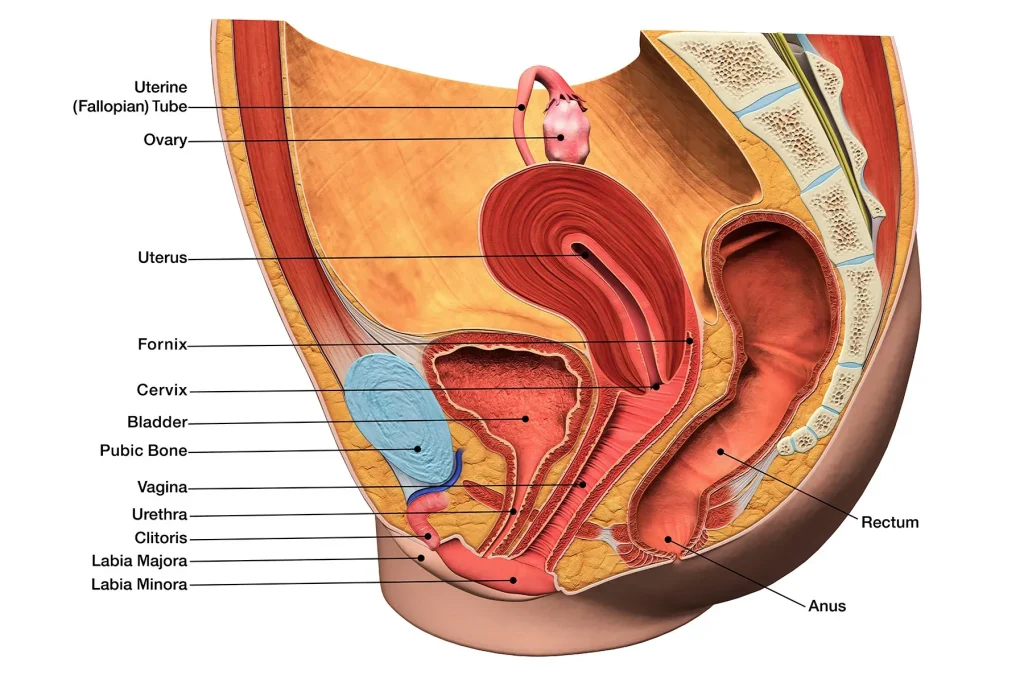
Before we dive into the science of self-insemination, it is important to have a basic understanding of the female reproductive system. The female reproductive system is made up of several organs and structures, including the ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, cervix, and vagina. These organs work together to produce and transport eggs, facilitate fertilization, and support the growth and development of a fetus.
Ovulation is a crucial part of the female reproductive cycle. Each month, one of the ovaries releases an egg into the fallopian tube, where it can potentially be fertilized by sperm. If the egg is not fertilized, it will pass through the uterus and out of the body during menstruation.
The Role of Sperm in Self-Insemination
In order for self-insemination to be successful, sperm must be present in the reproductive tract. This can be achieved through various methods such as using a sperm donor, partner’s sperm, or frozen sperm from a sperm bank. The sperm must then be collected and inserted into the vagina or uterus during the woman’s fertile window, which is the time when ovulation occurs.
The sperm’s journey begins in the vagina, where it travels through the cervix and into the uterus. From there, it enters the fallopian tube where it may encounter an egg. If the sperm is able to penetrate the egg and fertilize it, the process of conception begins.
Self-Insemination Techniques
Breaking the Biological Barrier: The Science Behind Self-Insemination for Single Women
There are several techniques that can be used for self-insemination, and the most commonly used method is using a syringe. This involves collecting sperm into a sterile syringe and inserting it into the vagina or cervix. Another method is using a cervical cap, which is a silicone cup that is placed over the cervix and filled with sperm. The sperm is then released into the cervix, where it can travel to the fallopian tubes.
Insemination kits are also available for purchase, which provide all the necessary tools for self-insemination. These kits usually include a syringe, cervical cap, and sometimes an ovulation predictor kit to help determine the most fertile time for insemination.
The Science Behind Self-Insemination
Self-insemination may seem like a simple process, but it involves a lot of science and precision in order to be successful. Timing is crucial, as the sperm must be inserted during the woman’s fertile window in order to have a chance of fertilizing an egg. Ovulation predictor kits can be helpful in determining the most fertile time for insemination.
Another important factor is the quality and quantity of the sperm used. Sperm must be collected and handled carefully in order to maintain its viability. It is also important to note that not all sperm is the same, and some may have better motility and morphology than others. This can affect the chances of successful fertilization.
The Risks and Benefits of Self-Insemination
Like any medical procedure, self-insemination comes with its own set of risks and benefits. One of the main risks is the potential for infection if proper hygiene and sterilization techniques are not followed. It is important to use sterile equipment and follow all instructions carefully to minimize this risk.
On the other hand, self-insemination offers several benefits for single women. It allows them to have control over their reproductive decisions and start a family on their own terms. It also eliminates the need for a partner or medical intervention, making it a more affordable option.
In conclusion, self-insemination is a viable option for single women who are looking to start a family. It involves a lot of science and precision in order to be successful, but with the right techniques and tools, it can be a safe and effective method. As society continues to evolve and embrace different family structures, self-insemination provides single women with the opportunity to break the biological barrier and become mothers on their own.
Probable Search Queries:
1. What is self-insemination and how does it work?
2. Can single women conceive without a partner?
3. What are the risks and benefits of self-insemination?
4. How does timing and sperm quality affect the success of self-insemination?
5. Where can I find resources and tools for self-insemination?